NEW VOCABULARY:
See off: Saying goodbye to someone because he goes on a trip.
Set off: To begin a journey or a trip.
Stop over: Stop overnight in a journey.
Speed up: To increase the velocity when driving.
ADRIAN PEREZ PORTFOLIO 4ºA
IESO TOMÁS BRETÓN
Sunday, June 16, 2019
SELF ASSESSMENT
This term think that I improve on all in comparison with the second. I didn´t enjoy a lot Abigail´s classes because they were at the bilingual hour. I need to improve in the vocabulary and I have to study more. This yearI have improve my english level so I´m proud of myself.
Monday, June 10, 2019
DIET
This diet is based on my calories.
I need 2973 kcal every day so I prepared my diet:
Breakfast:
I need 2973 kcal every day so I prepared my diet:
Breakfast:
-100g banana: 85 KCal 22,2g HC 1,1g Proteins 0,2g Fat
-150g whole milk: 118.5 KCal 15g HC 4,5g Proteins 4,5g Fat
Snack:
-100g pear: 56 KCal 14,8g HC 2,7g Proteins 0,2g Fat
-100g tuna in oil: 288 KCal 0 HC 24,2g Proteins 20,5g Fat
Food:
-100g pear: 56 KCal 14,8g HC 2,7g Proteins 0,2g Fat
-250g Chickpeas: 784 KCal 132g HC 44,7g Proteins 10,5g Fat
-250g Chicken: 425 KCal HC 45.5g Proteins 25.5g Fat
-50g rice: 171.5 KCal 39.3g HC 3.35g Proteins 0.125g Fat
Snack:
-100g apple: 58 KCal 15.2g HC 0.3g Proteins 0.2g Fat
-125g French bread: 336,25 KCal 71,925g HC 11,6g Proteins 0,25g
-100g tenderloin: 153 KCal 3g HC 23g Proteins 5g Fat
Dinner:
-100g banana: 85 KCal 22.2g HC 1.1g Proteins 0.2g Fat
-250g cod: 177 KCal HC 40.4g Proteins 0.7g Fat
-50g jelly: 150 KCal 0 HC 4,6g Proteins 0 Fat
Going from grams to calories, I have this results:
Total Calories=2953,8 kcal.
HC=347,42 x 4=1389,7 kcal.
Proteins=204,9 x 4=881 kcal.
Fats=68,075 x 9=612,7 kcal.
Sunday, March 17, 2019
SELF ASSESSMENT
This term I haven´t improved. I need to study more and I have worst marks than in the first term. During the term I have learnt about energy sources, phrasal verbs and other interesting things. I need to practise more the speaking presentation.
Thursday, February 28, 2019
VOCABULARY OF THE READING BOOK
-Pendant: a hanging ornament on a necklace.
-Gallows: A wooden structure used usually in the past, to hang criminals.
-Maid: A woman who works as a servant.
-Saddles: a seat for a rider on the back of a horse or other animal.
-Slammed: to shut with force and noise.
-Spanking: moving rapidly; quick and vigorous; brisk.
-Fits: To have a sudden attack of uncontrolled movements.
-Gasped: To breathe loudly and with difficulty.
-Spluttered: To talk rapidly and unclearly.
-Gallows: A wooden structure used usually in the past, to hang criminals.
-Maid: A woman who works as a servant.
-Saddles: a seat for a rider on the back of a horse or other animal.
-Slammed: to shut with force and noise.
-Spanking: moving rapidly; quick and vigorous; brisk.
-Fits: To have a sudden attack of uncontrolled movements.
-Gasped: To breathe loudly and with difficulty.
-Spluttered: To talk rapidly and unclearly.
VOCABULARY UNIT 3
-Chemical: a substance produced by or used in chemistry.
-Sustainable: Something able to continue over a period.
-Wireless: To use a system of radio signals rather than wires to connect computers, mobiles phones,
etc to each other.
-Boost: To improve or increase something.
-Sustainable: Something able to continue over a period.
-Wireless: To use a system of radio signals rather than wires to connect computers, mobiles phones,
etc to each other.
-Boost: To improve or increase something.
P.E WORK
Metabolism: refers to the processes your body uses to break down nutrients, form compounds the cells can use for energy and use those compounds to fuel cellular functions. Your body secretes enzymes to break down food into sugars, proteins, and fats. Then each cell of your body can take these in and use them in aerobic or anaerobic metabolic processes to form adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is the fuel used in the cell.
The calories from food are burned in this way to produce energy in each cell. Your body's overall metabolism includes muscle contraction, breathing, blood circulation, maintaining body temperature, digesting food, eliminating wastes, and the functions of the brain and nervous system. The rate at which you burn calories is called your metabolic rate.
Anaerobic metabolism: is the creation of energy through the combustion of carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. This occurs when your lungs cannot put enough oxygen into the bloodstream to keep up with the demands of your muscles for energy. It generally is used only for short bursts of activity, such as when you go for a sprint when running or cycling or when you are lifting heavy weights.When there isn't enough oxygen in the bloodstream, glucose and glycogen cannot be fully broken down to carbon dioxide and water. Instead, lactic acid is produced, which can build up in the muscles and degrade muscle function.
Aerobic metabolism: is the way your body creates energy through the combustion of carbohydrates, amino acids, and fats in the presence of oxygen. Combustion means burning, which is why this is called burning sugars, fats, and proteins for energy. Aerobic metabolism is used for the sustained production of energy for exercise and other body functions. Examples of exercises that use aerobic metabolism include walking, running, or cycling with sustained effort.
Here are the differences between anaerobic and aerobic metabolism:
-Aerobic respiration is the respiration which takes place in the presence of oxygen.
-The end products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water.
-The amount of energy released in aerobic respiration is very high.
-Anaerobic respiration is the respiration which takes place in the absence of oxygen.
-The end products of anaerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and ethanol or lactic acid.
-Anaerobic respiration helps in fermentation of yeast to produce ethyl alcohol or ethanol in beverage industry.
Here are a few useful facts about how anaerobic metabolism affects your body during exercise:
-Weight lifting and other strength exercises use anaerobic metabolism when providing strenuous effort in a short period of time.
-When running or cycling very fast your body turns to anaerobic metabolism to get enough energy.
-Sprinters' muscles use anaerobic metabolism to fuel their muscles during their short burst of speed.
-Anaerobic metabolism produces lactic acid, which can build up in the muscles to the point where you "feel the burn." This burning sensation is a normal side effect of anaerobic metabolism.
-Fast twitch muscle fibers rely more on anaerobic metabolism for quick contractions, but they fatigue more quickly as well.
-With high-intensity intervals, you can turn a normally aerobic exercise like endurance running into an anaerobic exercise as anaerobic metabolism is needed once you exceed 90 percent of maximum heart rate.
Friday, December 7, 2018
SELF ASSESSMENT
This term I have improved in translation and on the oral project, also I have done all the homework and I got worse in vocabulary and the grammar in the second exam. Im confused at nothing and the things that I liked the most are Abigails vocabulary and other activities. I need to improve in vocabulary.
Saturday, November 24, 2018
FNP
WHAT IS THE FNP?
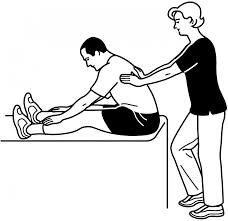
The FNP is a more advanced form of flexibility training that involves both a stretch and a contraction of the muscle group being targeted.
The FNP has four phases:
-You hold the muscle you want to exercise for 20 seconds.
-Six or eight seconds of agonist contraction.
-Three or five seconds to relax the muscle.
-Twenty seconds to stretch again the muscles.
Quadriceps FNP:

Hamstrings FNP:
General syndrome:
General adaptation syndrome is a three-stage response that the body has to stress.
 Threshold Law.
Threshold Law.
The threshold law is a claimed lawconcerning the effects of pharmaca or poisons in various concentrations. It states that: For every substance, small doses stimulate, moderate doses inhibit, large doses kill.
Training load:
Training load is a textual feedback on the strenuousness of a single training session.The main components of training load are volume and intensity. These must be increased to cause progressive overload and adaptation. Also, there is a trade-off between volume and intensity: in most cases, volume goes down as intensity increases and vice-versa.
Example:
Two players reached different training effect score from the workout (3.2 vs 4.0). All the interval sprints were performed in high intensity training zone (red). The reason was found from the heart rate recovery between the sprints. Player A recovered more quickly between the sprints whereas player B stayed in the high intensity training zone also during the recovery breaks.
Principles of training according to Oliver and Zintl:
The FNP is a more advanced form of flexibility training that involves both a stretch and a contraction of the muscle group being targeted.
The FNP has four phases:
-You hold the muscle you want to exercise for 20 seconds.
-Six or eight seconds of agonist contraction.
-Three or five seconds to relax the muscle.
-Twenty seconds to stretch again the muscles.
Quadriceps FNP:
Hamstrings FNP:
General syndrome:
General adaptation syndrome is a three-stage response that the body has to stress.
1: Alarm: Upon perceiving a stressor, the body reacts with a “fight-or-flight” response and the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated as the body’s resources are mobilized to meet the threat or danger.
2: Resistance: The body resists and compensates as the parasympathetic nervous system attempts to return many physiological functions to normal levels while body focuses resources against the stressor and remains on alert.
3: Exhaustion: If the stressor or stressors continue beyond the body’s capacity, the resources become exhausted and the body is susceptible to disease and death.

The threshold law is a claimed lawconcerning the effects of pharmaca or poisons in various concentrations. It states that: For every substance, small doses stimulate, moderate doses inhibit, large doses kill.
Training load:
Training load is a textual feedback on the strenuousness of a single training session.The main components of training load are volume and intensity. These must be increased to cause progressive overload and adaptation. Also, there is a trade-off between volume and intensity: in most cases, volume goes down as intensity increases and vice-versa.
Example:
Two players reached different training effect score from the workout (3.2 vs 4.0). All the interval sprints were performed in high intensity training zone (red). The reason was found from the heart rate recovery between the sprints. Player A recovered more quickly between the sprints whereas player B stayed in the high intensity training zone also during the recovery breaks.
Principles of training according to Oliver and Zintl:
Oliver:
-Principles related to the stimulation of physical conditioning.
- Principles related to the systems to which said stimulus is directed.
- Principles related to the response to said stimulus
Zintl:
- Those who initiate the adaptation.
- Those that guarantee adaptation.
- Those who exercise a specific control of adaptation.
- Those that guarantee adaptation.
- Those who exercise a specific control of adaptation.
Wednesday, November 7, 2018
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)